Plumbing
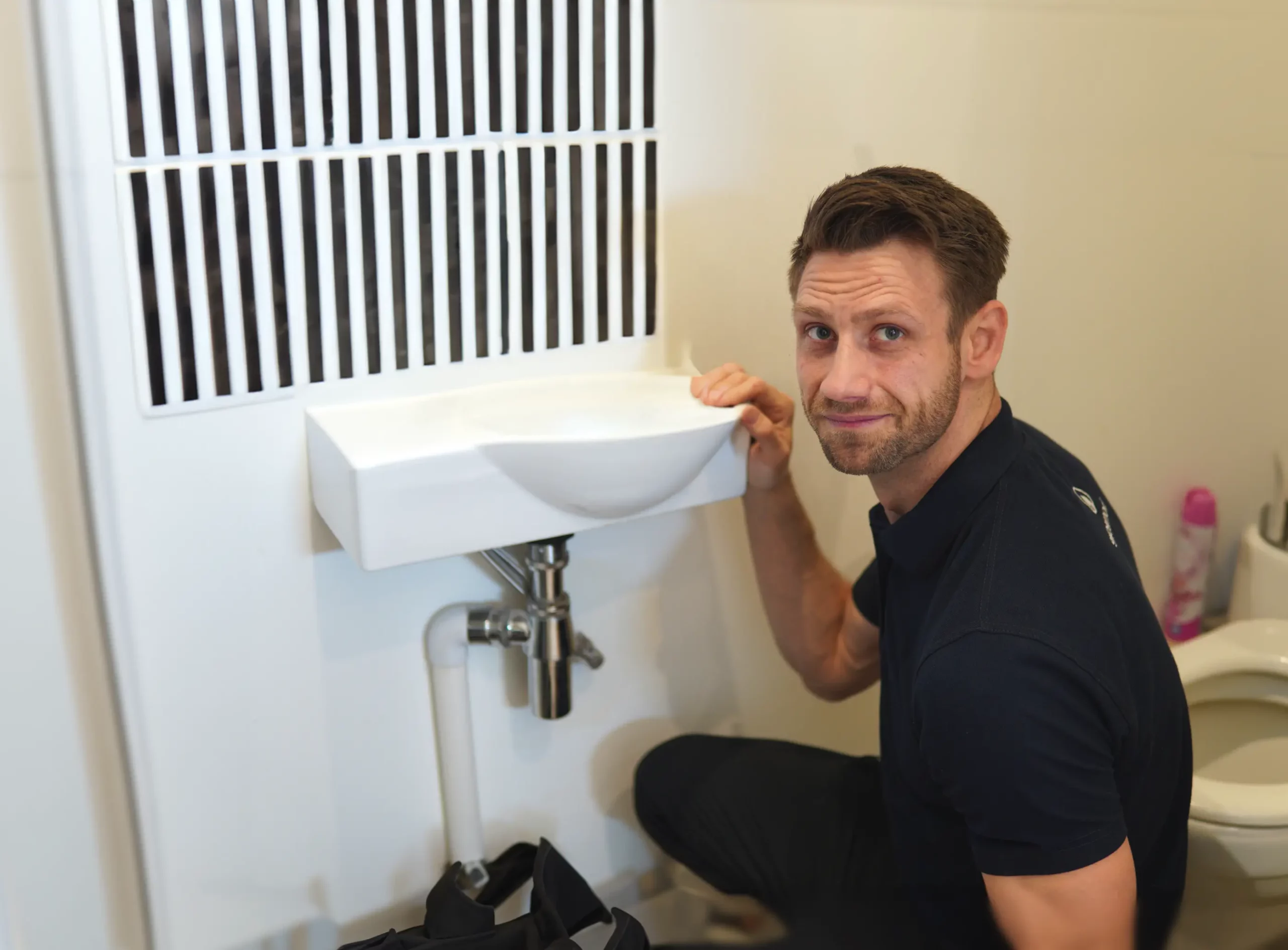
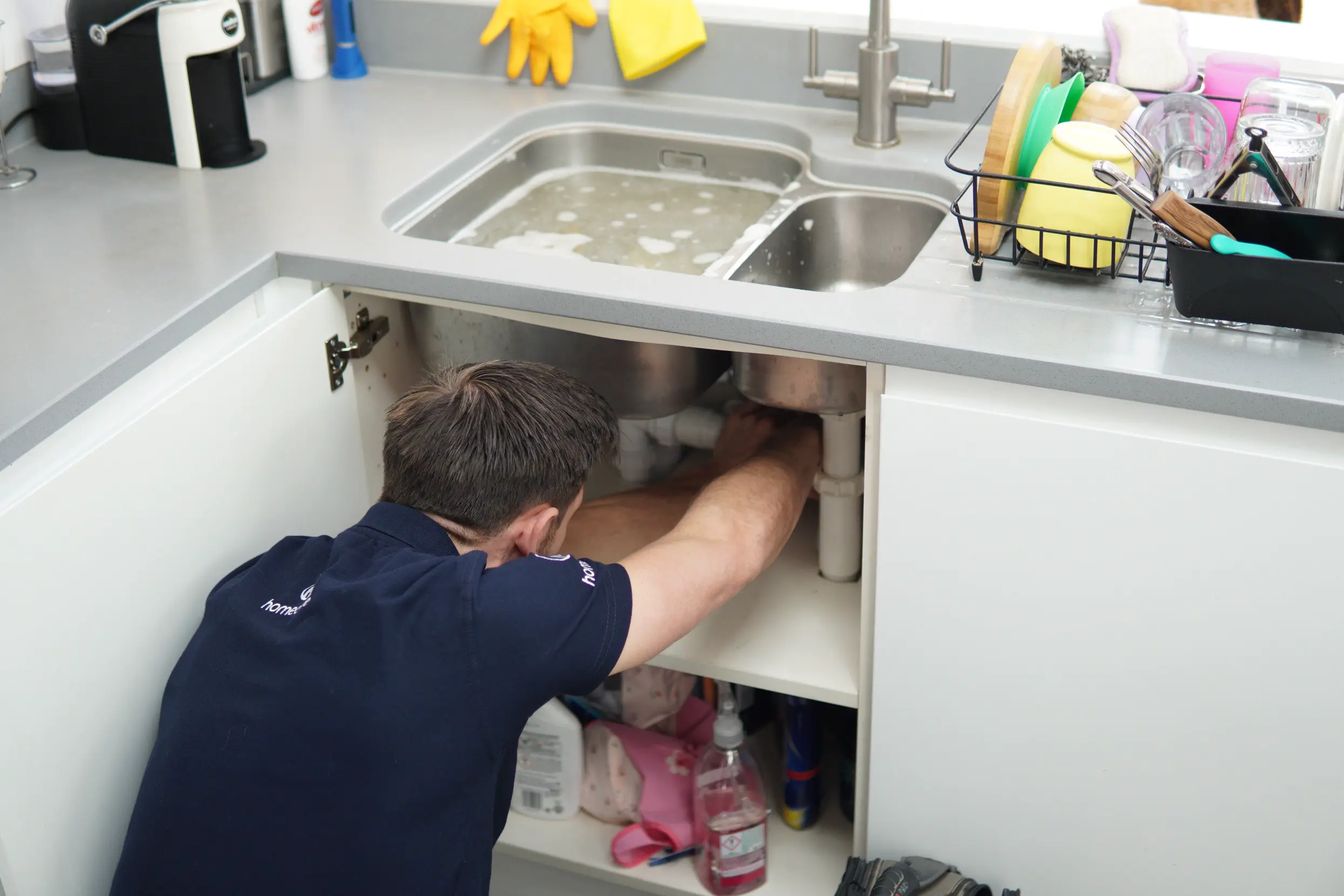
Plumbing services in London
No problem is too big for Homecure. Our plumbing services in London are available for emergency callouts and planned visits, keeping your plumbing system in perfect working order.
-
Available 24/7, 365 days
-
City & Guilds trained plumbers
-
Friendly and helpful service
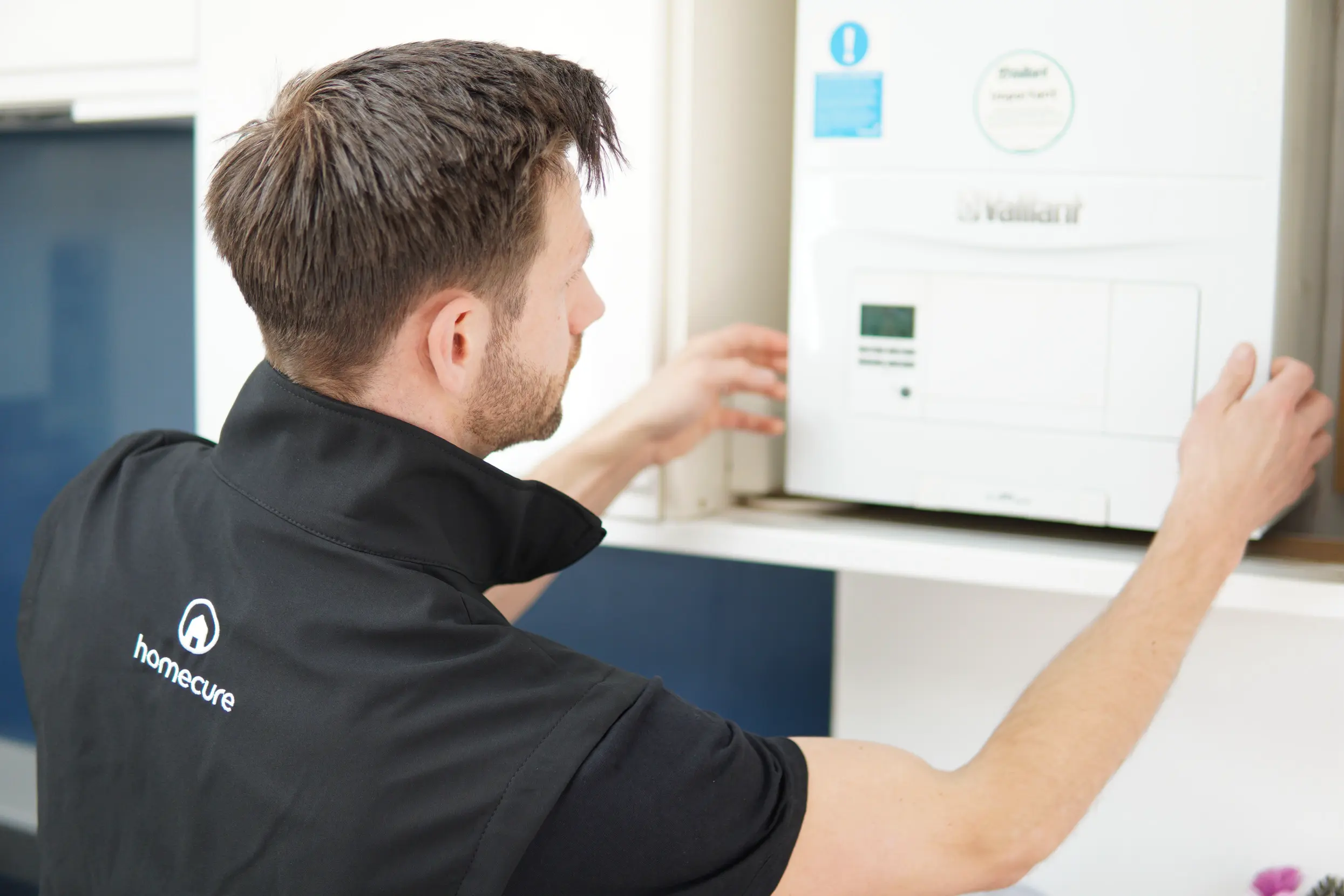
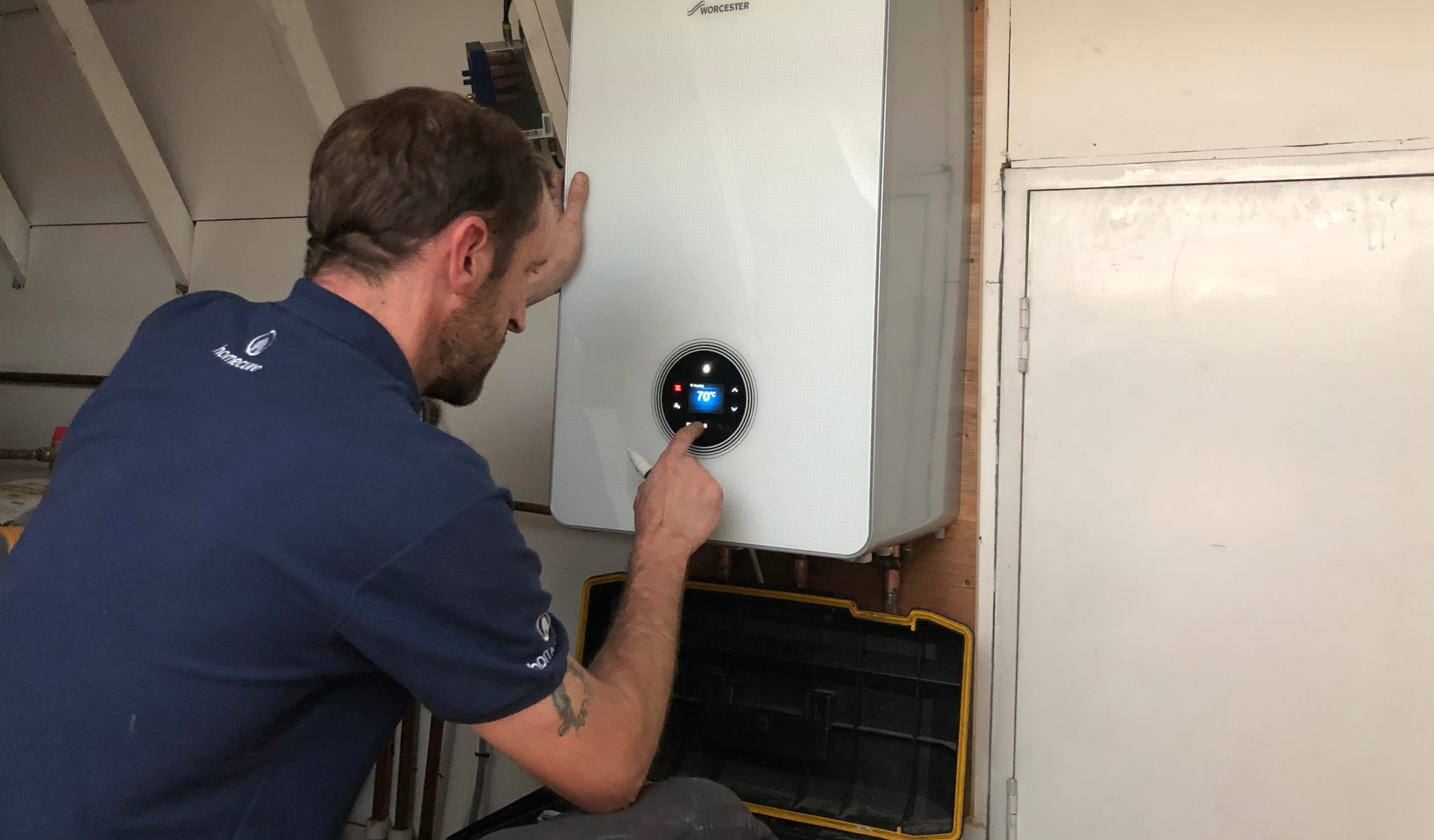
Boilers
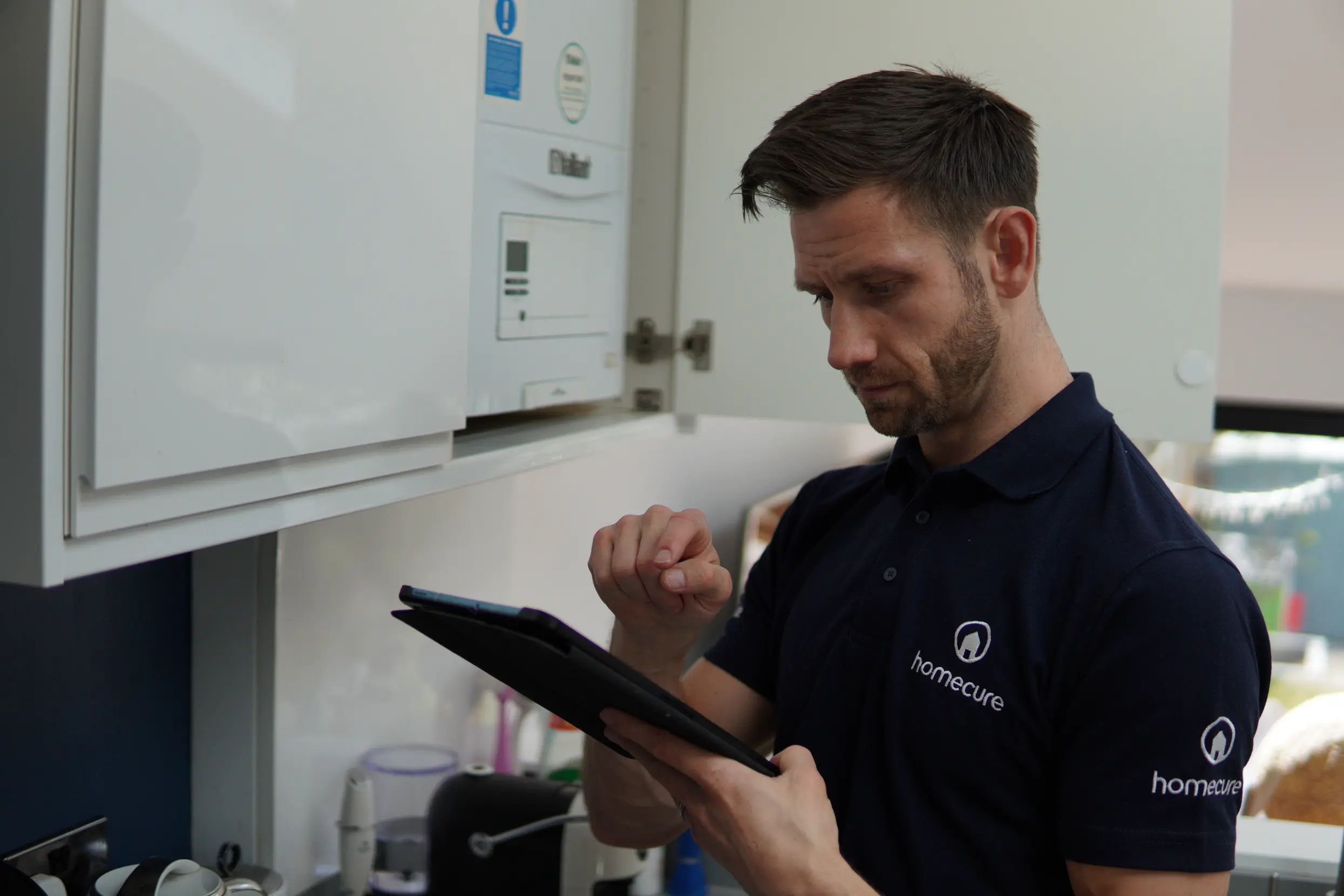
Boilers services in London
Our Gas Safe engineers are available to deal with any boiler-related issue. You can hire our boiler services in London 24/7, 365 days a year and we’ll be there within the hour.
-
Fully qualified and insured engineers
-
Available round the clock support
-
Ability to deal with any brand or type
Central heating
Heating services in London
Homecure’s Gas Safe engineers will ensure you stay warm right throughout the year. Our heating services in London are affordable, efficient and always customer-focused.
-
Reach us 24/7, 365 days
-
We’ll get to you within an hour
-
Repair and install a variety of heating systems
About
About Homecure Plumbers
We are passionate about what we do and pride ourselves on being able to offer a superior level of customer service, all while getting the best results possible for affordable prices.
Work Guaranteed
Same Day Service
Established in 2009
Certified Engineers